Introduction
The impact of social media on mental health is significant, as platforms like X, Instagram, and TikTok can shape our emotions and thoughts in profound ways. While social media fosters connection, overuse may trigger anxiety, low self-esteem, and sleep problems. This guide, updated as of May 16, 2025, examines how social media affects mental health and shares practical tips to minimize its negative effects, helping you maintain balance starting today.
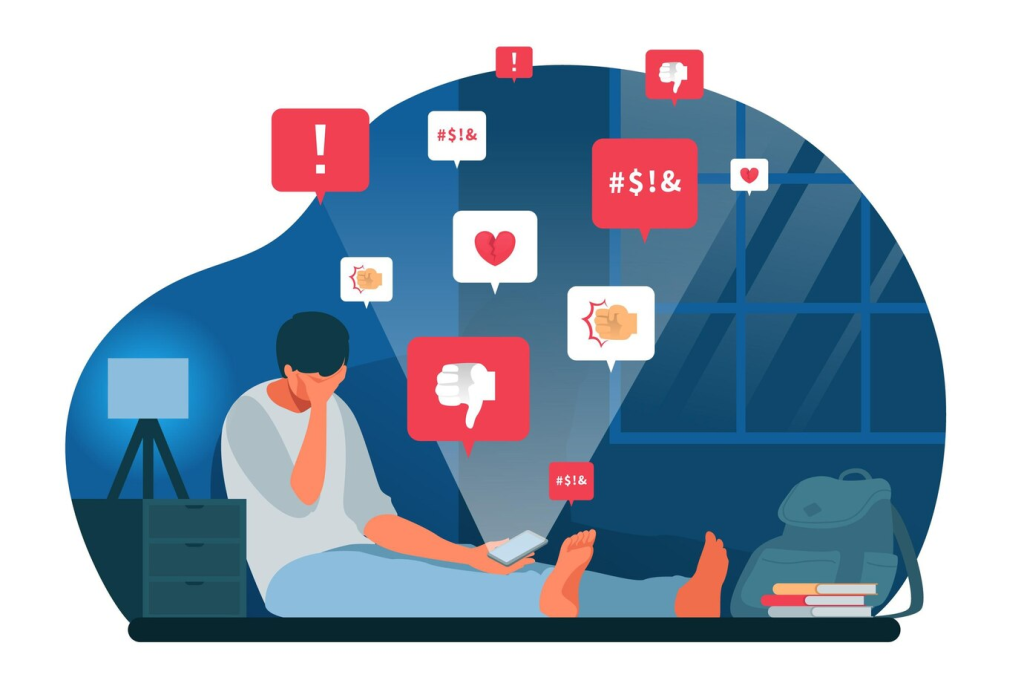

1. Increases Anxiety and Stress
Social media can heighten anxiety by bombarding users with news, opinions, or social pressures.
Triggers Overwhelm
Endless scrolling or comparing your life to curated feeds can spike stress. A 2023 study found 60% of teens felt anxious after heavy social media use.
Why It Works: Information overload and fear of missing out (FOMO) activate the brain’s stress response.
Pro Tip: Limit social media to 30 minutes daily using apps like Freedom to ease anxiety triggers.
2. Lowers Self-Esteem
Comparing yourself to idealized online images or lifestyles can damage your self-image.
Fuels Negative Self-Perception
Filtered photos or success stories on Instagram can make you feel inadequate. Research shows 70% of young adults report lower self-esteem after social media exposure.
Why It Works: Constant comparison distorts how you see yourself, amplifying feelings of inferiority.
Pro Tip: Follow positive accounts, like mindfulness or hobby pages, and unfollow those sparking envy.
3. Disrupts Sleep Patterns
Late-night scrolling or screen blue light can interfere with your ability to rest well.
Reduces Sleep Quality
Using social media before bed delays melatonin, making sleep harder. A 2024 study linked 2+ hours of nightly use to poor sleep in 65% of users.
Why It Works: Blue light suppresses sleep hormones, and engaging content keeps your brain alert.
Pro Tip: Set a phone-free hour before bed and use blue-light filters or night mode on devices.
4. Encourages Addictive Behaviors
Social media’s design, with likes and notifications, can foster compulsive use, impacting mental health.
Creates Dopamine Loops
Checking for likes or comments triggers dopamine, making you crave more. This cycle can reduce focus and increase irritability when offline.
Why It Works: Algorithms keep you engaged, mimicking addictive patterns.
Pro Tip: Turn off non-essential notifications and check social media at set times, like noon and 6 PM.
5. Amplifies Feelings of Loneliness
Despite online connections, social media can make you feel more isolated.
Reduces Real Connection
Superficial interactions, like likes or brief comments, may replace deeper bonds. Studies show heavy users report higher loneliness than moderate users.
Why It Works: Online interactions often lack the emotional depth of in-person relationships.
Pro Tip: Schedule weekly in-person meetups or calls with friends to balance online and offline socializing.
Conclusion
Social media’s mental health side effects, including anxiety, low self-esteem, sleep issues, addiction, and loneliness, can harm your well-being if unchecked. By limiting use, curating feeds, protecting sleep, managing notifications, and prioritizing real connections, you can enjoy social media safely. Start with one tip, like setting a screen-time limit, today, May 16, 2025, and nurture a healthier mind.
References
Psychology Today (2025). Social Media’s Impact on Mental Health. Available at: https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/social-media-mental-health.
Healthline (2025). How Social Media Affects Your Brain. Available at: https://www.healthline.com/health/social-media-mental-health-effects.
Verywell Mind (2025). Social Media and Mental Wellness. Available at: https://www.verywellmind.com/social-media-mental-health-issues.