In today’s fast-paced business environment, prioritization is key to achieving success. Consequently, businesses must focus on the most important tasks and efficiently manage workflows to stay ahead of the competition. Furthermore, prioritization not only helps with staying on track but also ensures that resources are allocated effectively. As a result, teams are able to improve their productivity and meet deadlines with greater efficiency. Teams must focus on the most important tasks and efficiently manage workflows to stay ahead of the competition. One system that has proven to be an invaluable tool for prioritization is the Kanban system. Originating from lean manufacturing and popularized by software development teams, Kanban offers a visually intuitive method to manage tasks and optimize workflows. In this article, we explore how Kanban systems teach us the art of prioritization and provide actionable insights for improving team productivity.
Understanding Kanban and Its Core Principles
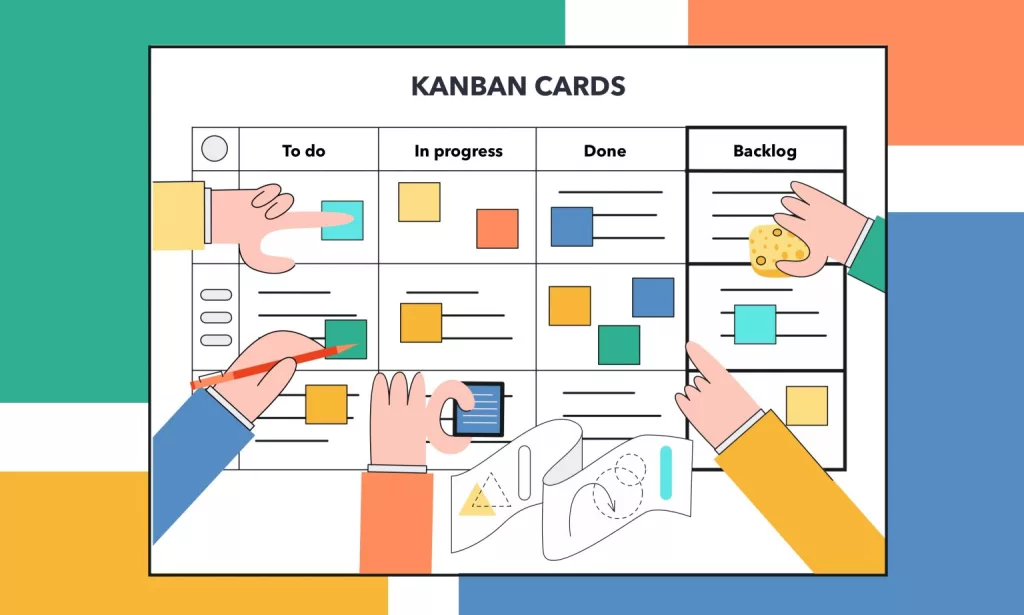
Kanban is a visual workflow management system that originated in Toyota’s production environment. Its primary goal is to optimize efficiency by managing work in progress (WIP) and minimizing bottlenecks. The system utilizes a board (physical or digital) where cards represent tasks. These cards move through various stages, such as To Do, In Progress, and Done.
Kanban works by visually showing the work items, the workflow, and the amount of work in progress. By focusing on these elements, Kanban helps teams prioritize work effectively and make data-driven decisions. In a Kanban system, there are a few key principles to understand:
- Visualize Work: Display all tasks and workflows to enable transparency.
- Limit Work in Progress (WIP): Restricting the number of tasks in each stage of the process prevents bottlenecks and improves task focus.
- Focus on Flow: Ensure work moves smoothly from one stage to another without unnecessary delays.
- Continuous Improvement: Foster a culture of ongoing adjustments and optimization.
These principles provide the framework that helps teams prioritize tasks and maximize efficiency.
The Role of Prioritization in Kanban
One of the greatest strengths of Kanban is its ability to help teams prioritize work effectively. Here’s how Kanban systems teach prioritization:
1. Visualizing Tasks to Identify Priority
A Kanban board visually represents tasks, allowing teams to quickly identify the most urgent tasks and those that can be deferred. Teams typically use cards or sticky notes to represent tasks on the board, with each card moving through different stages.
In terms of prioritization, the To-Do column is a great starting point. Teams can sort tasks in this column based on urgency or importance, making it clear which items need immediate attention and which can wait. By doing so, Kanban helps teams avoid decision fatigue and focus on what matters most.
2. Limiting Work in Progress (WIP)
By limiting the number of tasks in each stage, Kanban prevents teams from spreading themselves too thin and encourages them to focus on finishing tasks before taking on new ones. This principle teaches the importance of prioritizing quality over quantity.
For example, when a team reaches its WIP limit, it must finish a task before starting a new one. This prioritization method ensures that each task gets the necessary attention to completion. By preventing task overload, teams are better able to concentrate on delivering high-priority items without the distraction of multiple unfinished projects.
3. Focusing on the Most Important Work
Kanban encourages teams to tackle the most important or valuable work first. By displaying tasks on a Kanban board and categorizing them based on importance, teams can quickly assess the value of each task and decide which one to tackle first. Always move critical tasks to the front of the queue, and place less urgent items in the later stages of the board.
For example, software development teams might fix critical bugs before adding new features, ensuring they address the most significant issues first. This approach fosters a prioritization mindset, helping teams ensure that they’re always working on the most valuable tasks.
4. The Use of Classes of Service
Kanban systems can incorporate classes of service, a practice where tasks are categorized based on their priority level. Tasks might be classified as Expedited, Standard, Intangible, or Deferred.
- Expedited tasks are the highest priority, often requiring immediate attention.
- Standard tasks are the regular tasks that need to be done in a timely manner but don’t need urgent attention.
- Intangible tasks might be lower priority and are often related to future work or long-term goals.
- Deferred tasks are those that are placed at the bottom of the priority list, typically due to their low impact or value.
By categorizing tasks in this way, teams are able to prioritize effectively, ensuring that the most time-sensitive tasks are completed first.
5. Using Metrics to Improve Prioritization
Kanban systems emphasize data-driven decision-making. As teams use the board, they collect metrics like cycle time (the time it takes for a task to move from start to finish) and lead time (the time it takes for a task to move from the backlog to completion). These metrics help teams identify where they are spending the most time and which tasks are taking longer than necessary.
By analyzing these metrics, teams can adjust their workflows and prioritize the most efficient tasks. For instance, if a task is consistently delayed in a particular stage, the team can investigate and improve that part of the process.
6. Continuous Review and Adjustment
Another important aspect of Kanban is its focus on continuous improvement. Teams using Kanban systems regularly review their processes and assess how they can work more efficiently. This iterative approach encourages teams to revisit their priorities on a frequent basis, making it easier to adjust and respond to changes in workload, deadlines, or business needs.
For example, teams may adjust their WIP limits or introduce new classes of service as business conditions evolve, ensuring they’re always working in the most efficient way possible. Retrospectives and regular reviews allow teams to refine their prioritization practices and ensure that tasks are being handled in the most effective order.
Benefits of Prioritization in Kanban Systems
The prioritization techniques taught by Kanban systems have several key benefits:
- Improved Focus: By reducing multitasking and limiting the number of ongoing tasks, Kanban helps teams maintain focus and complete high-priority work efficiently.
- Better Resource Allocation: Kanban helps allocate resources to tasks that deliver the most value, avoiding waste and ensuring that resources are used optimally.
- Increased Flexibility: The visual nature of Kanban allows teams to respond to changes in priorities quickly, ensuring that they can adapt to evolving business needs.
- Faster Delivery: With fewer tasks in progress at any given time, work flows faster, and teams can deliver high-quality results more quickly.
Conclusion
Kanban systems offer powerful lessons in prioritization that can help teams increase efficiency, focus on high-value tasks, and adapt to changing needs. By visualizing work, limiting WIP, categorizing tasks by importance, and using data-driven metrics, Kanban enables teams to prioritize effectively and streamline their workflows. Whether in software development, manufacturing, or any other industry, implementing Kanban’s prioritization techniques can help your team work smarter, not harder.
References
- Anderson, D. J. (2010) Kanban: Successful Evolutionary Change for Your Technology Business. Blue Hole Press. Available at: https://www.amazon.com (Accessed: 18 July 2025).
- Liker, J. K. (2004) The Toyota Way: 14 Management Principles from the World’s Greatest Manufacturer. McGraw-Hill. Available at: https://www.amazon.com (Accessed: 18 July 2025).
- Poppendieck, M., and Poppendieck, T. (2003) Lean Software Development: An Agile Toolkit. Addison-Wesley. Available at: https://www.amazon.com (Accessed: 18 July 2025).






